
A considerable amount of product has entered the market over the past 10 years, with presumably some accumulating in households. With increasing recognition of the benefits of probiotics, the global market is expected to surpass US $52 billion by 2020 (Probiotics Market Size & Share 2019). 2017), lowering blood cholesterol (Simons, Amansec and Conway 2006) and impacting a range of other conditions (Tanner et al. 2010), reducing the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (Giannetti et al. They can potentially offer various benefits, such as preventing antibiotic-associated and traveler's diarrhea (Gao et al. Probiotics are ‘live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host’ (Hill, Guarner and Reid 2014) and are packaged and sold for use.

Consuming expired probiotics may not yield the benefits for which they were designed.Įxpired, probiotic, microbe, health benefit, packaging, storage BACKGROUND Despite some selected probiotic products retaining viability past their expiry date (indicating long-term storage is possible), the total counts were mostly well below that required for efficacious use as recommended by the manufacturer. All products with viable cells had the strain stipulated on the label. However, overall packaging type, storage conditions and time since expiry were found to affect viability. Product formulation and the number of species present did not appear to impact the stability of the products. While the products had a mean past expiration time of 11.32 (1–22) years, 22 still had viable contents, and 5 were within or above the original product cell count claim. The viable microbial cells were enumerated and representative isolates identified by 16S and internally transcribed spacer rRNA gene sequencing. Thirty-three expired probiotic products were evaluated, of which 26 were stored in conditions recommended by the manufacturer. Given that probiotics must be live microorganisms administered in adequate amounts, the aim of this study was to measure viability in expired products and assess how packaging and storage conditions impact efficacy, if at all. Inevitably, some of these products are used after expiration when microbial cell viability is below the recommended effective dose.

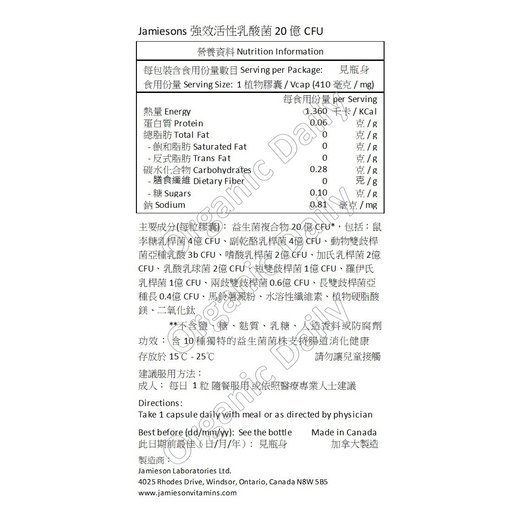
The popularity of using probiotics has surged, since they became widely accepted as safe and help improve general health.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
